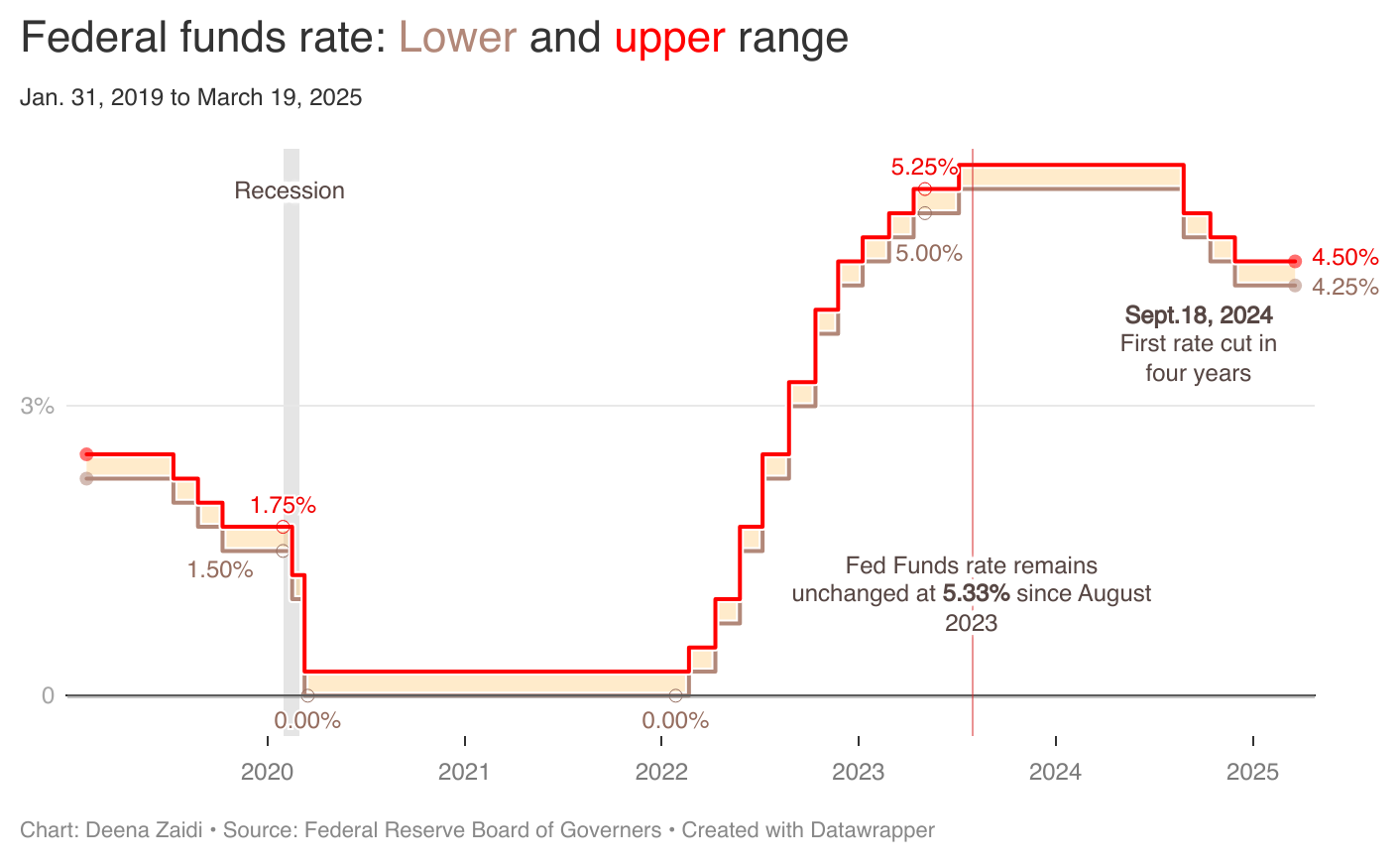
The Federal Reserve keeps its interest rate unchanged, maintaining its target range at 4.25% to 4.5%. When the Fed sets a target for interest rate, it commits itself to adjusting the money supply. To lower the Fed Funds rate, the Fed’s bond trades buy government bonds, increasing the money supply which in turn lowers the…