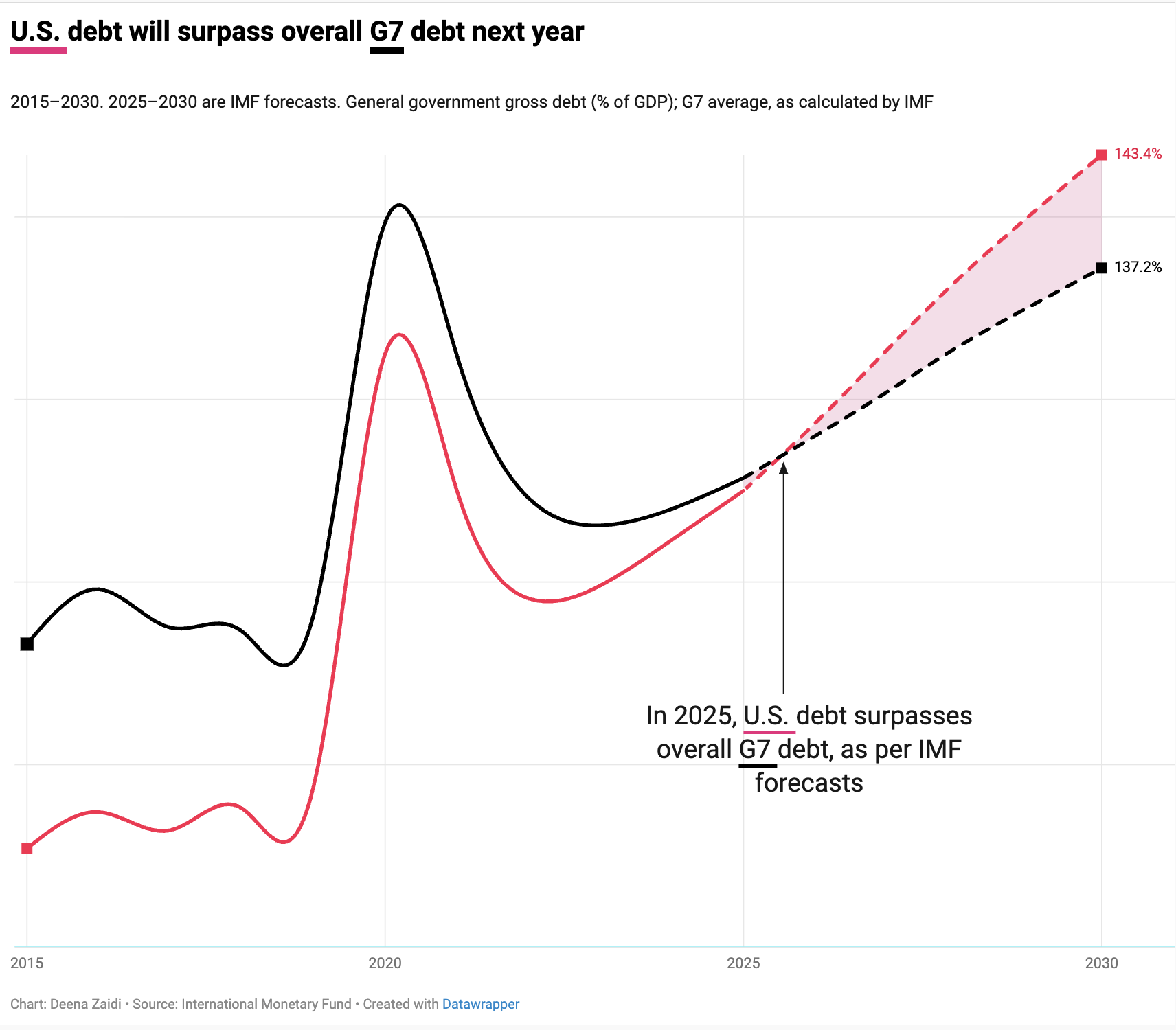
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projections show that by 2030, U.S. government debt as a share of GDP will exceed the G7 average and rank second-highest among the group, behind only Japan.
In the next 5 years, under the current fiscal trends continue the American debt is set to rise to 143% of GDP from 122% in 2024.
The U.S. gross federal debt has recently surpassed $38 trillion, marking one of the fastest trillion-dollar increases on record outside the COVID-19 period.
While debt levels vary across the G7, IMF projections show the U.S. on a steeper upward debt trajectory than most peers over the remainder of the decade.
The IMF projects a deterioration in the U.S. general government fiscal balance, reflecting higher interest costs, persistent primary deficits, and limited near-term fiscal consolidation, even as projected tariff revenues provide a partial offset.
🇺🇸 United States – Fastest projected increase in debt among G7 peers
• The U.S. gross government debt (debt held by all levels of government) is projected to rise sharply over the next few years.
• According to IMF World Economic Outlook projections, U.S. debt climbs from around 120–125% of GDP in the early 2020s to about 143.4% of GDP by 2030 under current policies- the steepest increase among G7 economies over this period.
🇯🇵 Japan – highest-debt country in the G7
• Japan remains an outlier with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the G7 by far (often above 200% of GDP).
• IMF data shows that Japan’s debt is far above its peers, both historically and in projected years.
🇮🇹 Italy – below the U.S., above most other G7 members
• Italy’s debt is high, but generally below that of the U.S. by 2030 — around ~137% of GDP.
• Italy’s debt remains elevated relative to most other G7 members.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom – well below U.S. and Italy
• The UK’s government debt ratio is projected to be above 100% of GDP but significantly lower than the U.S. and Italy by 2030. IMF forecasts it to remain around ~105% of GDP toward the end of the decade.
🇫🇷 France
• France’s debt remains high and is projected to range roughly between120–130% range by 2030 — consistent with general OECD/IMF analysis of advanced economy debt burdens. (France has historically run persistent deficits.)
🇨🇦 Canada – lower than most G7 peers
• Canada’s debt stays below most peers, typically around 100% of GDP or less, which the graph also reflects.
🇩🇪 Germany – lowest-debt G7 country
• Germany is noticeably lower than most other G7 countries, according to IMF data, with debt within 60–80% range — consistent with OECD definitions of general government debt.